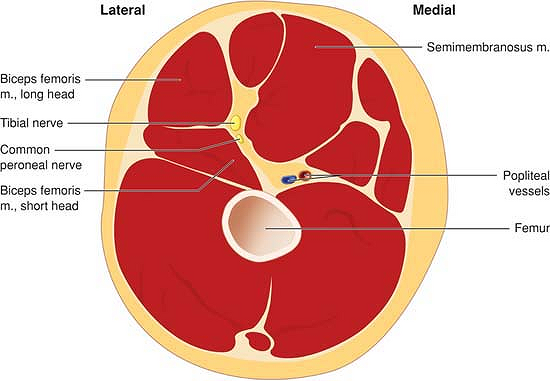
Ultrasound Guided Sciatic Block in the Popliteal Fossa
anterior to the hamstring muscles (semimembranosus, semitendinosus and
biceps femoris [long and short heads]), lateral to adductor magnus and
posterior and lateral to the popliteal artery and vein (Fig. 41-1).
At a variable level (approximately 5 to 10 cm above the popliteal
crease) the sciatic nerve divides into the tibial (medial) and common
peroneal (lateral) components. The tibial component becomes more
superficial as it moves distally accompanying the popliteal vessels in
the distal popliteal fossa. The common peroneal nerve moves laterally
to a position medial to the tendon of biceps femoris as it moves down
posterior and lateral to the knee. Since most foot and ankle surgical
procedures involve both tibial and common peroneal components of the
nerve it is essential to anesthetize both nerve components. Blockade of
the nerve before it divides therefore simplifies the technique.
the needle insertion point was at least 5 cm above the popliteal crease
to ensure block of both nerves. However, the use of ultrasound has
simplified that process by allowing us to follow the nerves and
determine exactly the level of division. Ultrasound therefore allows us
to accurately define anatomy prior to needle insertion and to choose a
needle insertion point that minimizes distance to the nerve from skin.
More importantly, local anesthetic spread can be directed in real time
allowing the nerve to be completely surrounded by local anesthetic.
been reported in the regional anesthesia literature. The sciatic nerve
is readily visible on ultrasound deep to biceps femoris and
semitendinosus and lies posterior and lateral to the femoral artery (Fig. 41-2).
The use of ultrasound removes the need to rely on surface landmarks and
the practitioner can choose the most convenient needle insertion point
based on the sonographic assessment of the anatomy.
 |
|
Figure 41-1. Gross anatomy of the popliteal fossa.
|
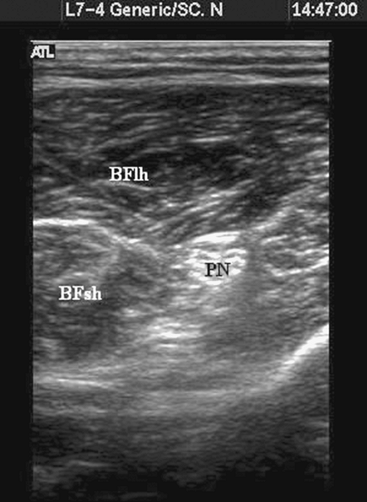
transverse plane so that the sciatic nerve appears as a circular
structure deep to biceps femoris (Fig. 41-2).
The easiest method for finding the sciatic nerve is to follow the
tibial nerve, which is a hyperechoic structure lying deep and lateral
to the popliteal artery at the popliteal crease, and follow this
hyperechoic structure until it is joined further proximal in the
popliteal fossa by the peroneal
nerve.
The sciatic nerve can be found directly above the popliteal fossa
without using this “mapping” technique by looking deep and medial to
the biceps femoris muscle and superficial and lateral to the popliteal
artery (Fig. 41-2).
 |
|
Figure 41-2.
Sonogram of the popliteal fossa 10 cm superior to the popliteal crease. PN, sciatic nerve in popliteal fossa; BFlh, biceps femoris long head; BFsh, biceps femoris short head. |
 |
|
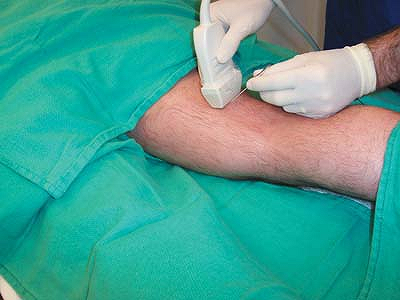
Figure 41-3. Photograph of the out-of-plane technique for ultrasound guided popliteal block in the transverse plane.
|
can be made. The out-of-plane technique is commonly used, is simpler,
and is less uncomfortable for the patient but does not allow
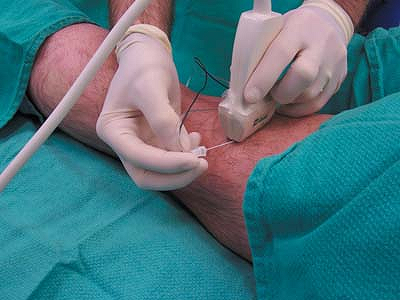
visualization of the needle shaft. Conversely, the in-plane technique
allows for needle shaft visualization but increases skin–nerve distance
and therefore patient discomfort. The lateral technique is useful
however for a patient who cannot lie prone.
contraction can be elicited if preferred by slowly increasing nerve
stimulator current until a twitch is seen (commonly less than 0.5 mA).
Once nerve identity is confirmed, local anesthetic is incrementally
injected. It is important to examine the spread of local anesthetic and
ensure that spread is seen encircling the nerve (Fig. 41-5).
Several needle positions may be needed to ensure adequate spread on
either side of the nerve. The nerve can often be seen more easily to
split
into tibial and common peroneal components after injection (Fig. 41-6).
The often-inadequate spread on injection with the needle in a fixed
position may explain why many popliteal blocks with apparently
excellent nerve stimulator endpoints fail even with large volumes of
local anesthetic.
 |
|
Figure 41-4. Photograph of the in-plane technique for ultrasound guided popliteal block in the transverse plane.
|
 |
|
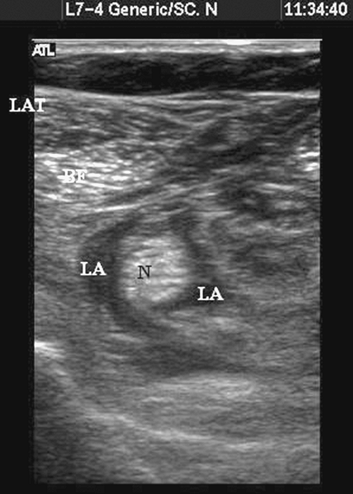
Figure 41-5.
Sonogram of the popliteal fossa postinjection with local anesthetic seen encircling the nerve. N, nerve; BF, biceps femoris; Lat, lateral; LA, local anesthetic spread. |
 |
|
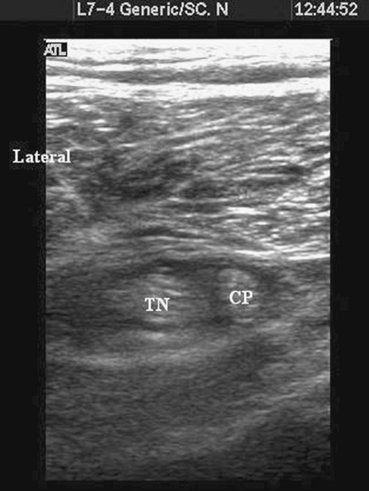
Figure 41-6. Local anesthetic (dark area)
seen encircling the two tibial and common peroneal nerves below the division of the sciatic nerve. TN, tibial nerve; CP, common peroneal. |
after performance of blind techniques indicates that despite
appropriate nerve stimulation endpoints at low currents (< 0.5 mA),
local anesthetic may not completely encircle the nerve. This may
explain the increased latency and high incidence of partial/failed
blocks with the blind popliteal technique. An ultrasound guided
technique can improve ability to encircle the nerve in local anesthetic
and improve block success.
anesthetic placement around the nerve appears to improve block onset
time and incidence of block success. Results from a
randomized-controlled study at Toronto Western Hospital indicate that
patients who have an ultrasound guided technique have both faster onset
and significantly increased efficacy compared to the blind technique.
Catheter placement is possible using both the posterior and lateral
approaches with the needle shaft being visible using the lateral
approach and a transverse view.
M, Rodriguez J, Alvarez J, et al. Sciatic nerve block via posterior
Labat approach is more efficient than lateral popliteal approach using
a double-injection technique: a prospective, randomized comparison. Anesthesiology 2004;101:138–142.
