Occipital Blocks
The cervical region is prepared and draped using sterile techniques.
Using fluoroscopy, the lateral view identifies the posterior arch of C1
vertebra (the atlas) and a dome shape between C1 and C2 dorsally. The
needle is placed parallel to the x-ray beam and advanced slowly. After
the position of the needle is confirmed by a lateral view, 1 to 2 mL of
water-soluble contrast media such as Isovue-200 (Bracco Diagnostics,
Princeton, NJ) is injected. This injection should not be associated
with any intravascular runoff or epidural or subarachnoid propagation.
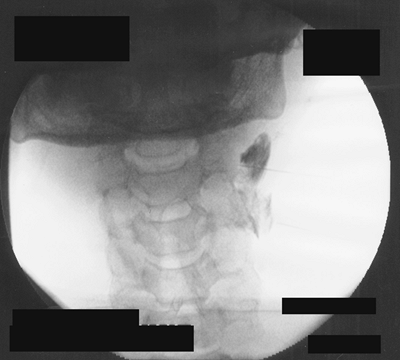
The local anesthetic mixture is slowly injected. An anteroposterior
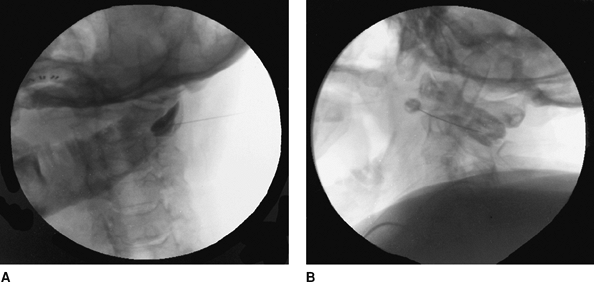
view (Fig. 65-1) is taken and the needle is advanced to the midfacet line between the C1 and C2 vertebrae. Figure 65-2 presents an oblique view.
 |
|
Figure 65-1. C2 selective nerve block; anteroposterior view.
|
 |
|
Figure 65-2. An oblique view.
|
-
A working intravenous line and standard monitoring is essential.
-
Appropriate resuscitation equipment is essential.
-
Continuous monitoring equipment is essential to all procedures.
-
Do not allow patients to walk back to
their rooms. They should be transported on a stretcher and monitored
for 45 to 60 minutes afterward.
Diagnostic or therapeutic block for the diagnosis and treatment of
occipital headache, occipital neuralgia, pain in the distribution of
the greater and lesser occipital nerves, and postherpetic neuralgia.
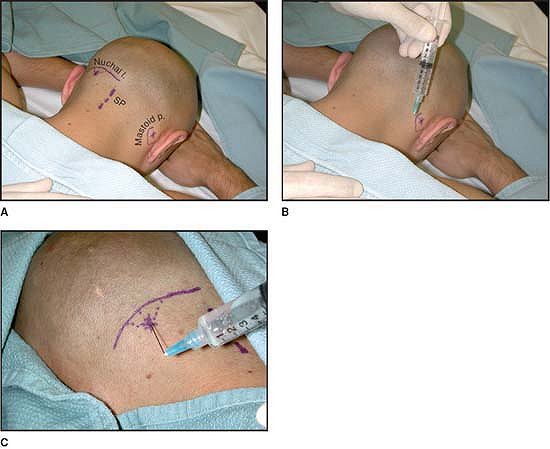
The lesser occipital nerve arises from the ventral rami of the third
cervical nerve and innervates the lateral portion of the posterior
scalp and
pinna of the ear. The nerve is blocked in the region of the mastoid process (Fig. 65-3B).
The greater occipital nerve arises from the dorsal rami of the second
cervical nerve and supplies the posterior medial aspect of the scalp to
the vertex of the head. The nerve is blocked at the level of the
superior nuchal ridge (Fig. 65-3C).
 |
|
Figure 65-3. Anatomic landmarks for greater and lesser occipital nerve block.
|
After sterile preparation of the region, the needle is introduced
perpendicular to the periosteum and advanced superiorly after making
contact with bone. After negative aspiration, the local anesthetic
mixture is injected in a fan distribution while withdrawing the needle.
